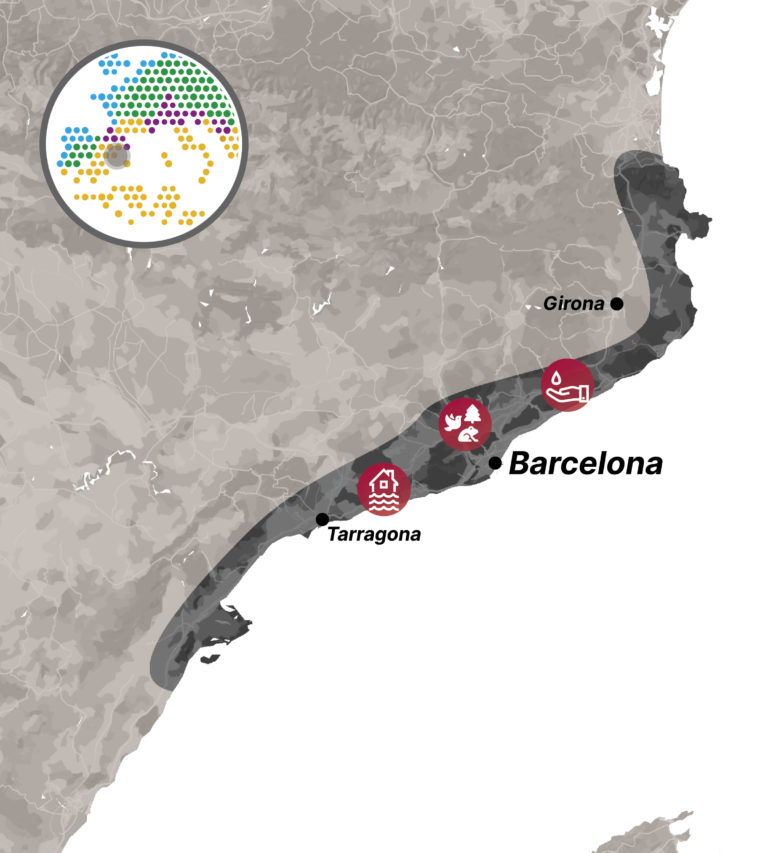
The Catalan coast in northeastern Spain spans 600 km and has a wide range of geographical and biodiversity systems that provide vital ecosystem services. While representative of other Mediterranean coastal regions, this area is particularly significant due to its concentration of tourism, natural and societal dynamics, economic activities, urbanization, agriculture, and critical infrastructure.
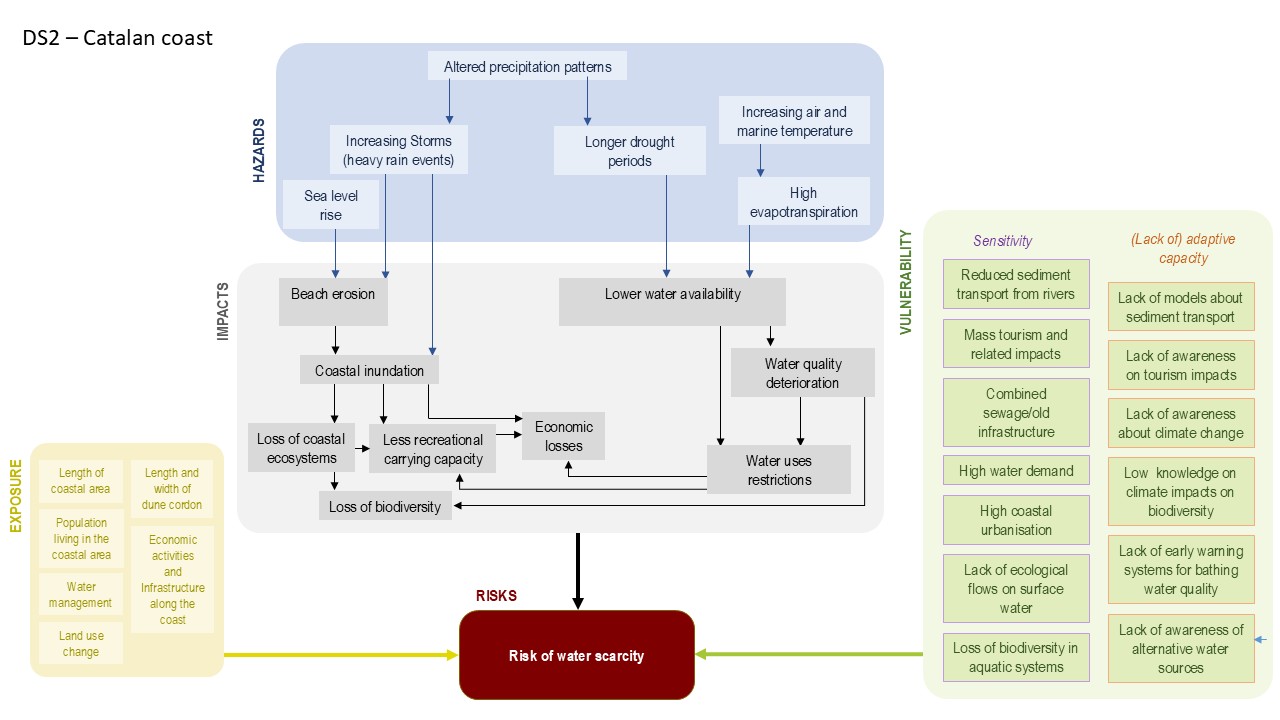
Current climate trends indicate an increasing risk of various climate hazards, including rising temperatures, sea level rise, extreme marine storms, and reduced precipitation. These changes are likely to exacerbate the impact on coastal flooding, coastal erosion, biodiversity loss, and water scarcity.
The Impetus Coastal Resilience Knowledge Booster provides tools, methodologies, guidelines, and use case examples with results of eight adaptation measures that have been field-tested in different locations in the region. The final goal of the RKBs is to promote the upscaling and mainstreaming of adaptation measures in similarly vulnerable bioregions affected by climate change.