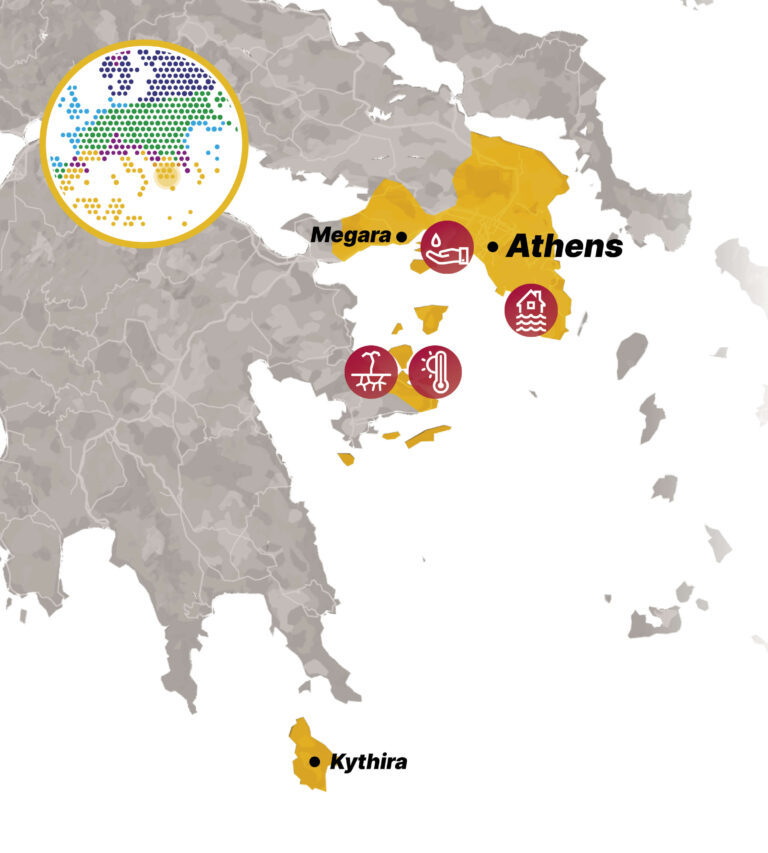
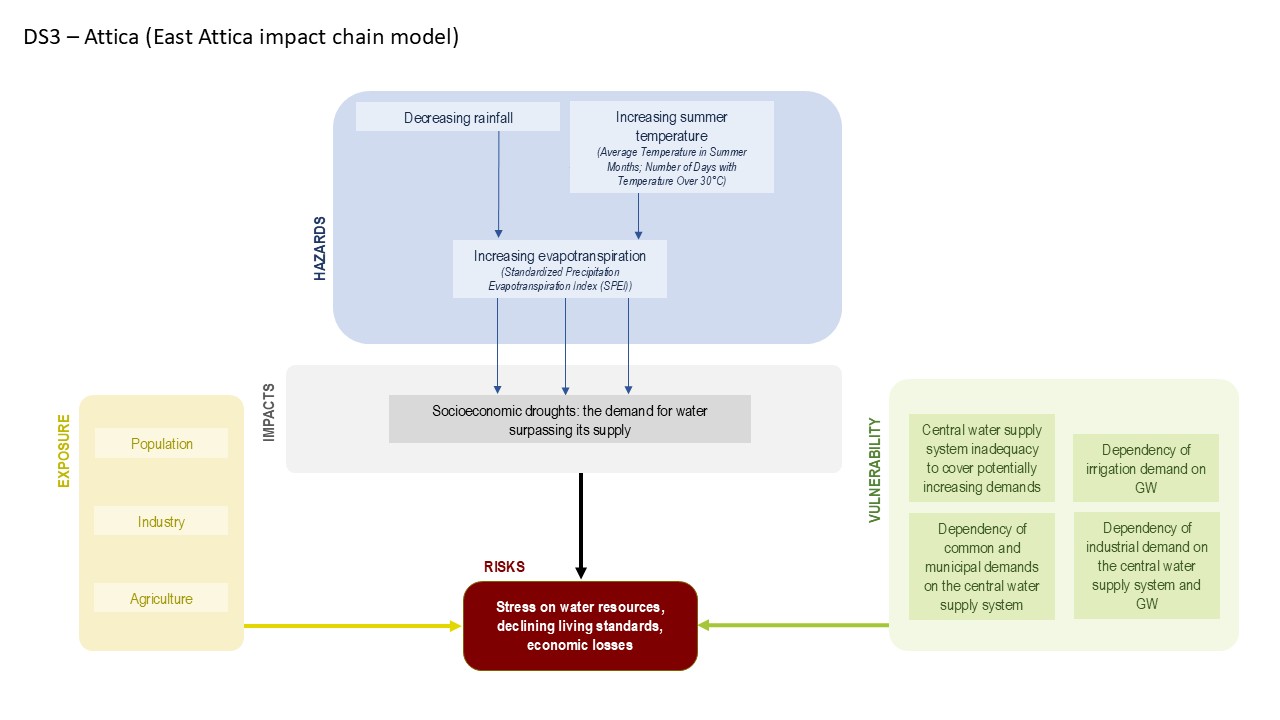
The growing population of Athens, combined with rapid urbanization, tourism, and agricultural demands, has significantly increased water consumption, placing immense pressure on already limited resources. This demand, together with inadequate infrastructure in certain areas, further exacerbates water scarcity. Overexploitation of both surface and groundwater has led to the depletion of local sources and, in coastal regions, the risk of seawater intrusion into aquifers. Additionally, water quality is increasingly threatened by pollution from agricultural runoff (fertilizers and pesticides), untreated wastewater, industrial discharges, and urban runoff.
To address these pressing challenges, scalable and transferable solutions are needed, focusing on water recycling and reuse, resource efficiency and conservation, advanced decision-support tools, stakeholder engagement, public awareness, and policy enhancement.